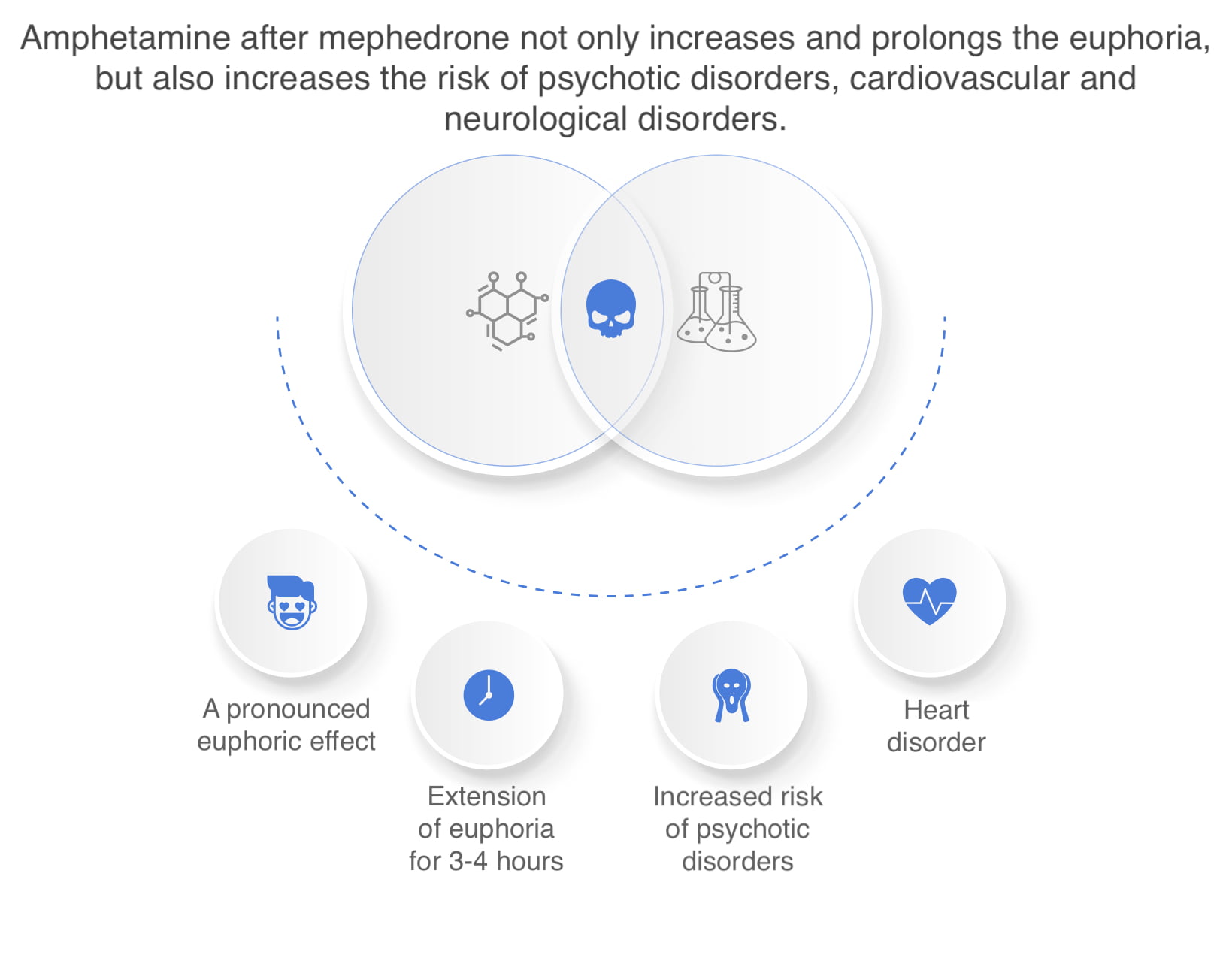
Narcotic psychostimulants increase mental and physical performance, improve mood, and relieve fatigue and depression. In an effort to get even more pronounced euphoria and stimulation, drug addicts mix psychoactive substances in various combinations. A mixture of mephedrone and amphetamine is a new but already quite common mix. It is often practiced sequential drug use, when the effect of the first prolongs and intensifies the second.
Amphetamine was first synthesized in 1887 and was long used as a drug to treat asthma, narcolepsy, obesity and depression. The drug became widespread after World War II, and by 1960 it was actively used as a narcotic. The first description of mephedrone was published in 1929, but the psychostimulant did not find a use for a long time. Since 2008-2010, it has been actively produced in clandestine laboratories and distributed among drug addicts.
Is the combination of mephedrone and amphetamine lethal?
Mephedrone and amphetamine are psychostimulants, whose mechanism of action is based on increasing the activity of dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine in the nervous system. These compounds affect the receptors located in the centers of the brain that are responsible for motor and mental activity, positive emotions, learning, communication functions. Therefore, the main effects are stimulating, euphoric and empathogenic.
Mephedrone is believed to be more of a euphoric and amphetamine a stimulant.
The difference between mephedrone and amphetamine is the duration of action. The structure and pharmacodynamics of amphetamine are well understood. Its molecule is a phenethylamine with a methyl group in the alpha position. Mephedrone is a chemical modification of amphetamine that has a ketone in the beta position. Because of this particular structure, the drug penetrates more easily through the blood-brain barrier, but has less of an effect on the nervous tissue. That is why its effects are more intense but less long lasting than those of amphetamine.
Combined use of amphetamine and mephedrone
The combination of two psychoactive substances increases the probability of forming a stimulant psychosis – an acute mental disorder with hallucinations, paranoia, delusions and inadequate behavior. The duration of such a condition is on average 1-3 days, less often several weeks or months. Terms depend on individual features of nervous system and quantity of the taken drugs.
Symptoms of amphetamine psychosis include auditory and visual hallucinations, delusions of persecution and delusions of relation simultaneously with clear consciousness and extreme agitation, sometimes there may be some signs of psychic automatism syndrome (Kandinsky-Clerambo syndrome). At the same time, the person experiences tension and anxiety. Hallucinations are, as a rule, true, but pseudo-hallucinations can also be observed. Sometimes a micro-hallucinatory-paranoid syndrome is encountered, as with cocaine use. It manifests as hallucinatory sensations of small insects on the body, or worms, dots, threads.
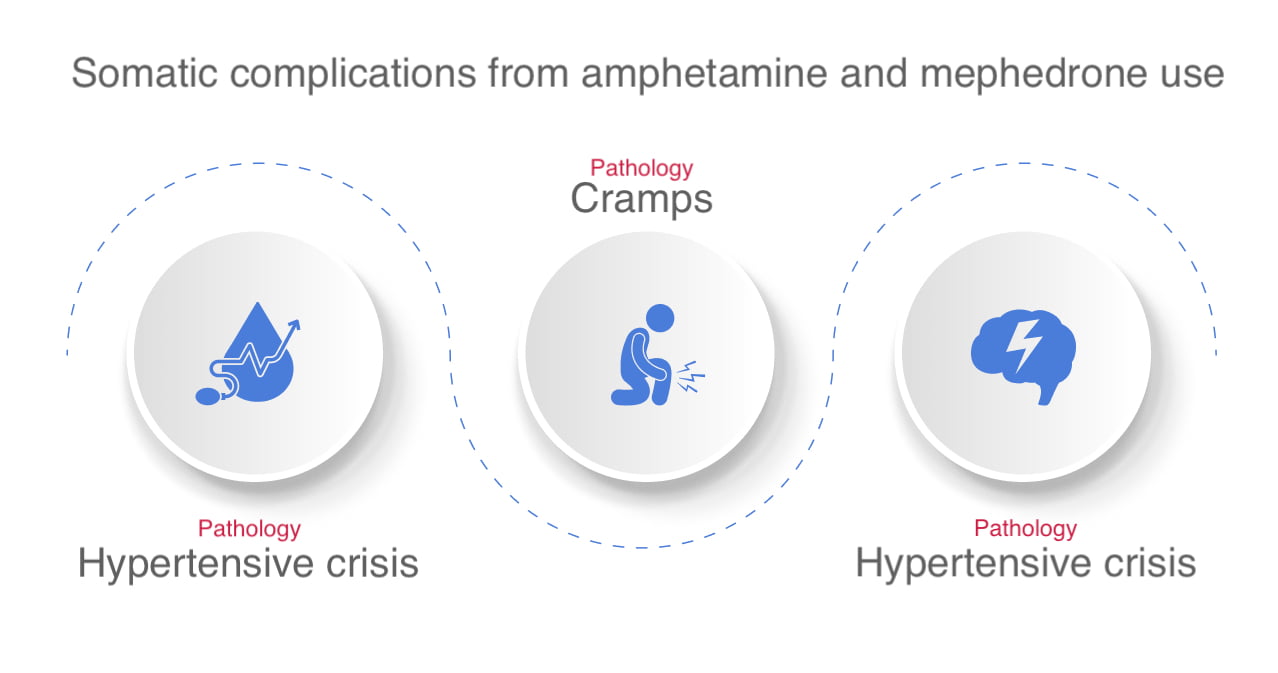
In the light of the above facts there is quite a logical question: what is more harmful – amphetamine or mephedrone? There is no unequivocal answer to this question, especially since the long-term effects of mephedrone have not yet been studied. But when used together, psychostimulants cause a more intense (than when used in isolation) strain on the cardiovascular and neuromuscular system. The risk of developing the following pathologies increases:
- Hypertensive crisis. Abrupt increase of blood pressure up to 180/120 mm Hg and more is accompanied by life-threatening lesions of internal organs. Ischemic stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, aortic dissection are possible.
- Seizures. Psychostimulants increase excitement in the nervous system, but reduce the content of calcium and sodium – trace elements necessary for normal nerve conduction, regulation of muscle tension and relaxation. This imbalance leads to involuntary painful contraction of the skeletal muscles.
- Convulsive seizures. Increased general excitation in the structures of the brain can provoke the formation of individual pathological foci of activity, similar to those observed in patients with epilepsy. An epileptiform seizure with tonic-clonic convulsions develops.
Conclusions
Psychostimulants increase the side effects of each other, so the risk of stimulant psychosis, hypertensive crisis, seizures and other complications increases.